[Lecture Summary] 00 Algorithm and Data Structure : Overview
This contents is based on Lecture of link
Insights
- All the algorithm and Data Strucutre seeks to make efficient environment through separating operating loops
- Express in an inductive way and prove it!
- It’s better to define properties, featrues in a recursive structure!
Philosophy
What we need to know about is
- how to solve computation problems
- Just like binary relation, there are edges between inputs and outputs
- What we need to concern about is Scalability, Generalizability for arbitrary sized inputs
- how to communicate
- being proving correctness and arguing efficiency
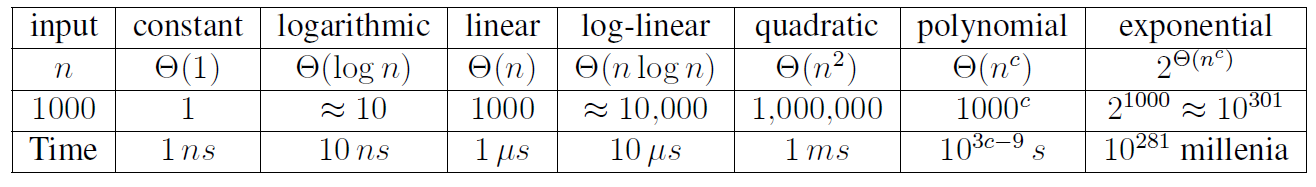
🔥 Asymptotic Notation
Upper bound $O(\cdot)$
Lower bound $\Omega(\cdot)$
both, tight bound $\theta(\cdot)$
🔥 Amortized Analysis
When it comes to measure cose over many or sequence of operations, we can say amortized cost $T(n)$ if k operations cost at most $kT(n)$.
In this case, we say $T(n)$ amortized having a meaning of averaged cost over operations
Model of Computation(Word-RAM, Machine word)
Properties
- Handle w bit sized data
- EX. 64bit for CPU and corresponding mem size is 16 exabyes!
- This determines how long the address is so that it can access data in a constant time(Random Access!)
- w is always bigger than $\log(n)$
- w is about CPU(how it process) and $\log(n)$ is about RAM
- Support constant time operators
Algorithm
Procedure mapping each input to a single output!
(= It is about how to solve problem!)
Correctness
= How can we convince ouself whether it is correct or not?
= Induction or inductive proof
= Find base case upon inductive Hypothesis and generalize it case of k
Efficiency(Run time, complexity analysis)
Compare with others! But… It does depend on the performance of H/W.
That’s why it is better to measure fundamental operations rather than time.
The level of “efficiency” is dependent on the context but we can consider polynomial time with respect to the input size as an efficient algorithm.
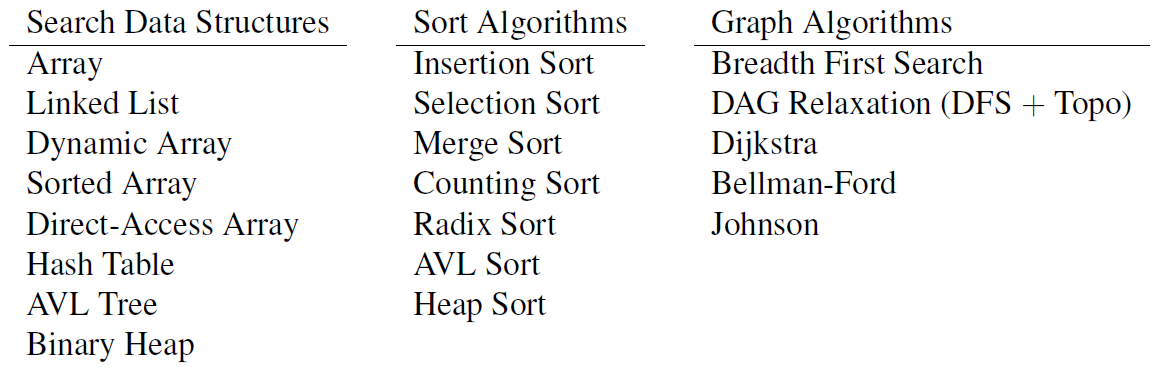
Data Structure
Any structure that can store data and support a series of operations! More details will be covered in the following articles.
(For preliminaries) There are 2 kinds of interface that data strcuture can support
- Set Interface : Intrinsic order(based on items keys)
- Sequence Interface : Extrinsic order
One thing is that, Data Structure “support” operations which implies that it is relevant to solution about how to store and implement. On the other hand, Interface is a specification which is about what the operation works or how we can store data!
댓글남기기