[Lecture Summary] 11 Algorithm and Data Structure : Graph Problems
This contents is based on Lecture of link
Problem to be solved
There are lots of problems in graph structured data. The thing is that we need to know about I/O for each problem and corresponding algorithm! When it comes to understanding algorithm, we need to prove correctness from the point of view of target problem and I/O.
Topological Sort
- Topological Order
ordering $f$ of vertices such that every edge $(u,v)$ satisfies $f(u)<f(v)$
- Finishing Order
order completed Full-DFS vertices.
completed vertex comes first
KEY! If G is Directed Acyclic Graph(DAG), reverse of a finishing order is topological order.
Personally, we can interprete as follows:
topologically far vertex is the latest recursion! Therefore, reverse of a finishing order is order of topoligically distance.
Cycle Detection
For directed graph, we can detect cycles in graph. This is available because for every DAG, the above statement satisfies. That is, if graph is not DAG, then every directed graph but not an acyclic graphs which contains cycles cannot satisfy that statement.
To return cycles, trace ancestor(or parent) in Full-DFS. In sumamry, use topological sort to check whether there exist cycles or not and Full-DFS to specify cycles.
Input : Graph
Output : cycles
Algorithm : Full-DFS
Connected Component
parition of $V$ into subsets which subgraph for corresponding subset is connected.
Input: Graph
Output: Component
Algorithm : Full-BFS or Full-DFS
Singel Pair Reachability
Input : Graph, source node $s$ and target node $t$
Output : bool
Singel Source Reachability
Input : Graph, source node $s$
Output : bool for all $v \in V$
Algorithm : DFS or BFS
Single Pair Shortest Path
Input : Graph, source node $s$ and the other node $t$
Output : distance $\delta(s,t)$ and shortest path in G
Single Soursce Shortest Paths
Input : Graph, source node $s$
Output :
distances for all $v \in V$ and shortest path tree(or parent pointer) which contains shortest path from $s$ to every $v \in V$
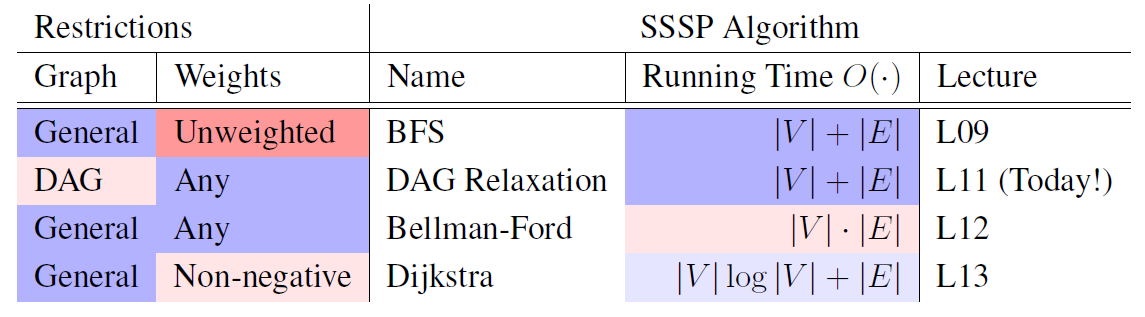
Algorithm :
Shortest Path Tree
For weighted graph, algorithm return only parent pointer of $v$ with finite distance from source vertex $s$ as result of shortest path tree.
Input : Graph
Output : Parent pointer
Algorithm:
- Initialize empty parent pointer data structure P
- Set P(s) = None
- For each vertex $u$ whose distance is finite
- For each $v \in Adj^+(u)$
- If P($v$) is empty, $P(v) \gets u$, $\delta(s,v)=\delta(s,u) + w(u,v)$
- For each $v \in Adj^+(u)$
The thing is that we can compute parent pointers afterwards, so all we need to compute is distance in the algorithm
Simple Shortest Paths
We say simple shortest paths when graph does not contain negative weight cycles! It implies that there does not exist any vertex which is visited more than once.
If distance from $s$ to $v$, there exists a shortest path to $v$ that is simple.
Finite shortest paths contain at most $\mid V \mid - 1$ edges. This works as upper bound! SO simple paths constraint in runtime analysis.
댓글남기기